简介与概念
Spring Cloud Stream 是一个用于构建消息驱动微服务的框架。Spring Cloud Stream 基于 Spring Boot,整合消息中间件(Kafka或RabbitMQ) 构建可独立运行,生产级的Spring应用。
应用模型
一个Spring Cloud Stream应用程序依赖于于独立的消息中间件。应用通过Spring Cloud Stream注入的输入和输出通道与外部世界通信。通道通过专用的Binder实现与外部代理连接。这种模型屏蔽了消息中间件的使用差异,我们只需掌握Spring Cloud Stream的使用就可以方便的构建消息驱动的微服务应用。
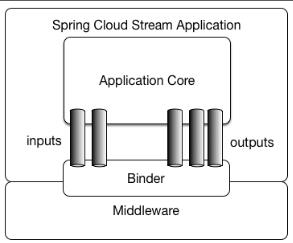
Binder
Binder 是 Spring Cloud Stream 的一个抽象概念,是应用与消息中间件之间的粘合剂。目前 Spring Cloud Stream 实现了 Kafka 和 Rabbit MQ 的binder。
通过 binder ,可以很方便的连接中间件,可以动态的改变消息的
destinations(对应于 Kafka 的topic,Rabbit MQ 的 exchanges),这些都可以通过spring.cloud.stream.binder进行配置。
发布订阅模型
Spring Cloud Stream 使用了经典的发布/订阅模式。发布者将消息发布到指定的Topic中,订阅者通过订阅该Topic来消费消息。
Consumer Group
类似于Kafka中消费者组的概念,每个binding可以指定一个group,一条消息只会被同一个group中的一个binding消费。可以被用来防止重复消费。可以于spring.cloud.stream.bindings.<channelName>.group中定义。
搭建Kafka与Zookeeper
为了在本地构建我们的第一个Spring Cloud Stream应用,我们需要先行搭建其依赖的Kafka。Kafka又需要用到Zookeeper。这里使用Docker Compose来快速搭建Kafka与Zookeeper。
编写 Docker-compose.yml
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| version: '3'
services:
kafka:
image: wurstmeister/kafka
container_name: kafka-streamlistener
ports:
- "9092:9092"
environment:
- KAFKA_ADVERTISED_HOST_NAME=192.168.99.100
- KAFKA_ADVERTISED_PORT=9092
- KAFKA_ZOOKEEPER_CONNECT=zookeeper:2181
depends_on:
- zookeeper
zookeeper:
image: wurstmeister/zookeeper
ports:
- "2181:2181"
environment:
- KAFKA_ADVERTISED_HOST_NAME=zookeeper
kafka-manager:
image: sheepkiller/kafka-manager
ports:
- 9000:9000
environment:
ZK_HOSTS: zookeeper:2181
KAFKA_BROKERS: kafka:9092
|
启动配置好的Docker-compose
之后前往 http://192.168.99.100:9000验证 Kafka 运行情况
构建 Spring Cloud Stream 应用
本例中,我们将构建两个微服务,Producer开放Restful接口,并将接口请求发布至消息队列。Sample订阅队列并打印其中的消息。
引入依赖
首先在两个项目中引入依赖
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| <dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-stream-kafka</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.junit.vintage</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-vintage-engine</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-stream-test-support</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
|
在 Spring Boot 中配置 Spring Cloud Stream 的 binder 与 bindings
Consumer的application.yml
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| spring:
cloud:
stream:
kafka:
binder:
brokers: 192.168.99.100:9092
default-binder: kafka
bindings:
msg_output:
destination: msg
binder: kafka
error_output:
destination: error
binder: kafka
|
Consumer的application.yml
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| server:
port: 8080
spring:
cloud:
stream:
kafka:
binder:
brokers: 192.168.99.100:9092
default-binder: kafka
bindings:
msg_input:
destination: msg
binder: kafka
error_input:
destination: error
binder: kafka
|
Producer编写
定义binding接口
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| public interface Producer {
String OUTPUT_CHANNEL ="msg_output";
String ERROR_CHANNEL ="error_output";
@Output(Producer.OUTPUT_CHANNEL)
MessageChannel messageOutput();
@Output(Producer.ERROR_CHANNEL)
MessageChannel errorOutput();
}
|
开启binding注解
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| @SpringBootApplication
@EnableBinding(Producer.class)
public class StreamproducerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(StreamproducerApplication.class, args);
}
}
|
定义Controller接收请求并置入消息队列
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| @RestController
@RequestMapping("/")
public class Controller {
@Resource
Producer producer;
@RequestMapping("/msg/{key}")
public String sendMsg(@PathVariable String key, @RequestBody Object msg){
Map<String,Object> payload = new HashMap<>();
payload.put(key,msg);
producer.messageOutput().send(MessageBuilder.withPayload(payload).build());
return "sent";
}
@RequestMapping("/error/{key}")
public String sendErr(@PathVariable String key, @RequestBody Object err){
Map<String,Object> payload = new HashMap<>();
payload.put(key,err);
producer.errorOutput().send(MessageBuilder.withPayload(payload).build());
return "sent";
}
}
|
Consumer编写
定义binding接口
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| public interface Consumer {
String INPUT_CHANNEL ="msg_input";
String ERROR_CHANNEL ="error_input";
@Input(Consumer.INPUT_CHANNEL)
SubscribableChannel messageInput();
@Input(Consumer.ERROR_CHANNEL)
SubscribableChannel errorInput();
}
|
使用@StreamListener注解消费消息
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| @EnableBinding(Consumer.class)
public class Receiver {
@StreamListener(Consumer.INPUT_CHANNEL)
public void getInput(Map<String,Object> msg){
System.out.println("[msg]: "+msg.toString());
}
@StreamListener(Consumer.ERROR_CHANNEL)
public void getError(Map<String,Object> error){
System.out.println("[err]: "+error.toString());
}
}
|
结果
Producer请求
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| {
"msg":"hello",
"uid":"3319"
}
{
"error":"ERROR",
"uid":"2113"
}
|
Consumer输出
1
2
| [msg]: {msg1={msg=hello, uid=3319}}
[err]: {error1={error=ERROR, uid=2113}}
|
References
